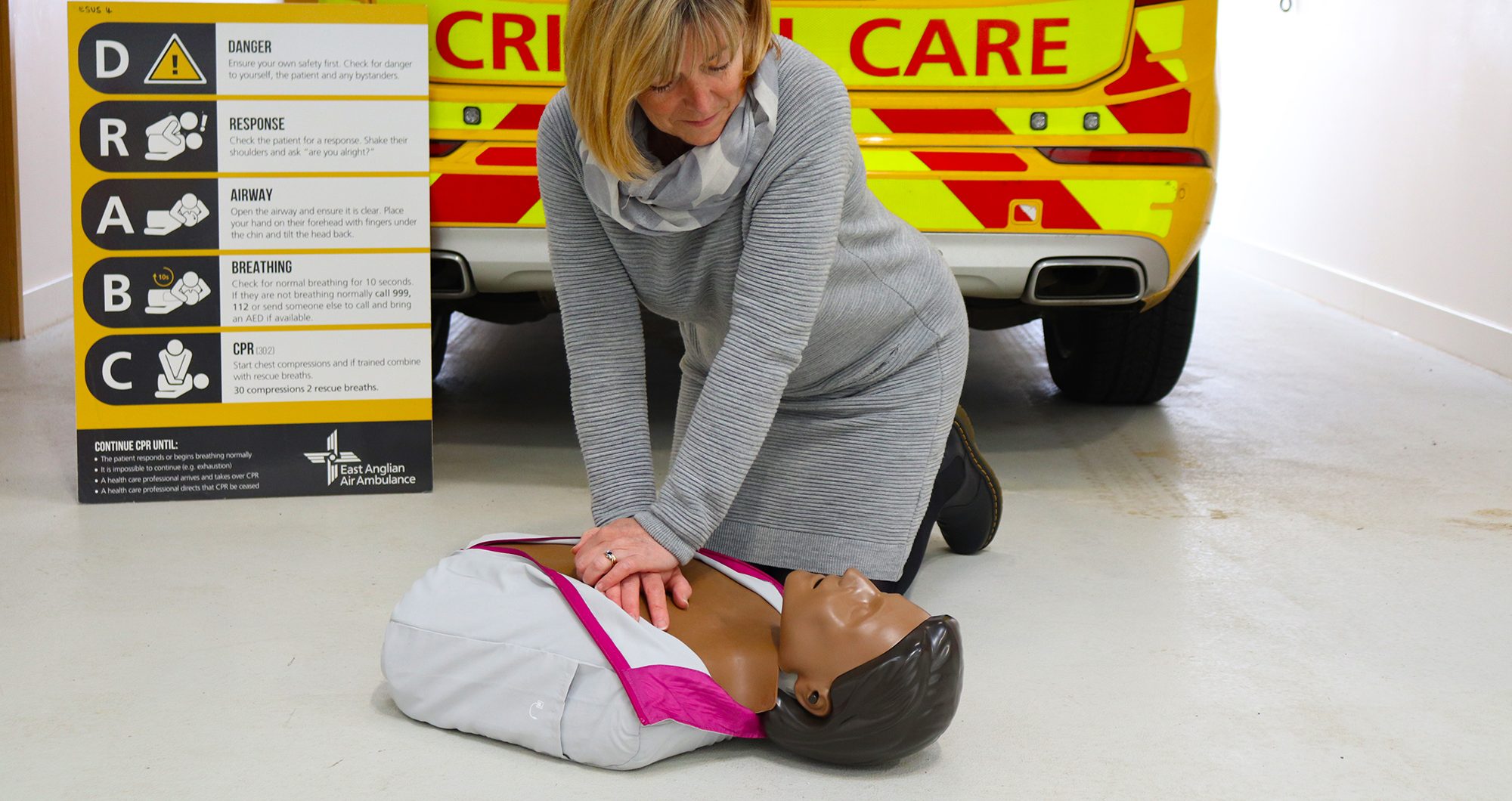
What's the difference between a heart attack and a cardiac arrest?
It is important to understand the difference between a heart attack and a cardiac arrest so you can take the correct necessary actions to increase somebody’s chances of a positive outcome.
Heart Attack
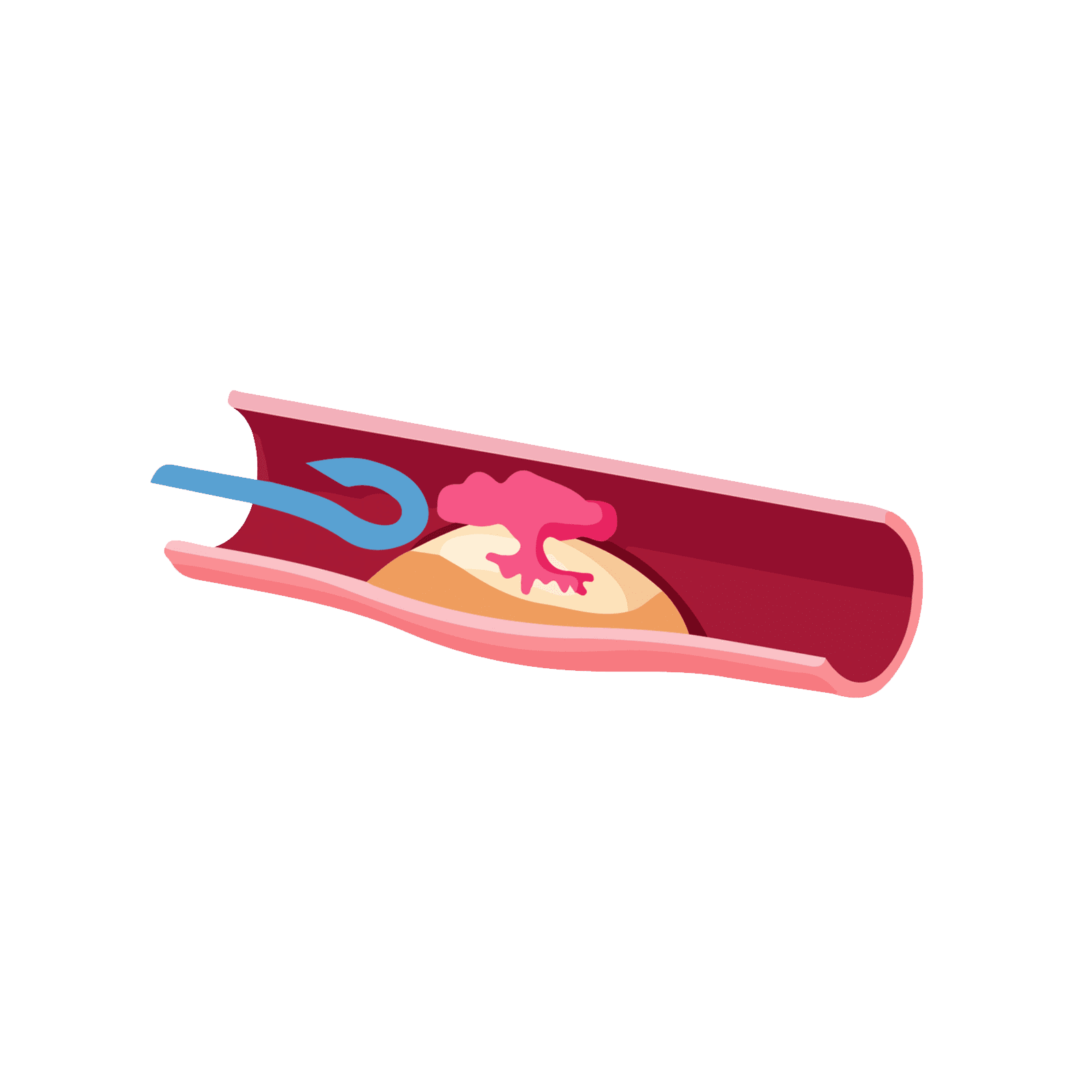
In simple terms, a Heart Attack is a blood problem within the heart wall. It is a circulation issue caused by a blocked artery. The person will most likely be conscious and breathing.
The heart is a muscle and, like all parts of the body, especially hard-working muscles, it requires its own blood and oxygen supply. If some of the blood vessels in the wall of the heart get blocked, part of the heart muscle may die, and the person may have a heart attack. A heart attack can, in some cases, lead to a cardiac arrest, so it is important to get medical help to the person as soon as possible.
Common symptoms of a heart attack:
- Pain or tightness in the chest.
- Pain down one arm, in the neck or jaw, or in the back.
- Stomach pain, like indigestion.
- A sense of impending doom.
- Profuse sweating.
- Difficulty breathing.
- A change in colour.
ACTION: Call 999.
(Image credit- Heart Foundation.org)
Cardiac Arrest
A cardiac arrest is a life-threatening emergency where the heart stops beating and stops pumping blood around the body, preventing it getting to vital organs, particularly the brain. The person will be unconscious and not breathing, or not breathing normally, noticeably a ‘gasping’ reflex caused by the brain not receiving enough oxygen. This is known as ‘agonal’ breathing.
There are different reasons why this can happen, including a heart attack where the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle become blocked. This can result in abnormal electrical activity in the heart. With a patient suffering this type of cardiac arrest, a defibrillator can shock the heart back into a normal rhythm.
Someone having a cardiac arrest will become unconscious very quickly.
Not everyone who is unconscious has had a cardiac arrest (other things can cause unconsciousness, including seizures, for example). Therefore, it is important to check an unconscious person for normal breathing. If they are not breathing normally, they are having a cardiac arrest.
ACTION: Call 999 and start CPR.
(Image credit- Heart Foundation.org)